Course Offerings - Design technology
IB DP Design Technology SL & HL
The Diploma Programme (DP) Design Technology course aims to develop internationally minded individuals who enhance their understanding of design and the technological world to facilitate a sustainable future. The course is engaging, accessible, inspiring, and rigorous, incorporating a multidisciplinary approach that integrates science, mathematics, humanities, and the arts. It can count as either a Group 4 or Group 6 subject for the IB Diploma.
The core philosophy of the course is design thinking, which enables students to:
- Understand users, challenge assumptions, and redefine complex problems.
- Engage in experimental and inquiry-based learning.
- Develop solutions that balance theoretical and practical limitations.
- Incorporate empathy, ideation, prototyping, and testing in problem-solving.
Content
Core Content SL/HL
A: Design in Theory
B: Design in Practice
C: Design in Context
Practical Programme (Design Project (IA) + Collaborative Sciences Project)
Key Topics
A: Design in Theory
- People: Ergonomics, user-centered research methods.
- Process: Prototyping techniques, IB DP design process.
- Product: Material classification, introduction to structural, mechanical, and electronic systems (HL only).
- Production: Manufacturing techniques (HL only).
B: Design in Practice
- User-Centered Design (UCD) and prototyping.
- Material selection, structural systems, mechanical/electronic systems (HL only).
- Production systems (HL only).
C: Design in Context
- Ethical and Social Responsibilities of designers.
- Inclusive design and sustainability.
- Life Cycle Analysis and Circular Economy (HL only).
Assessment
The assessment for Design Technology SL & HL consists of internal and external components.
Paper 1 – Multiple-choice questions
Paper 2 – Short-answer & extended-response questions
Internal Assessment – Individual Design Project (50 hours of works)
Grading SL • Internal assessment 40% • External Assessment 60%
Grading HL • Internal assessment 30% • External Assessment 70%
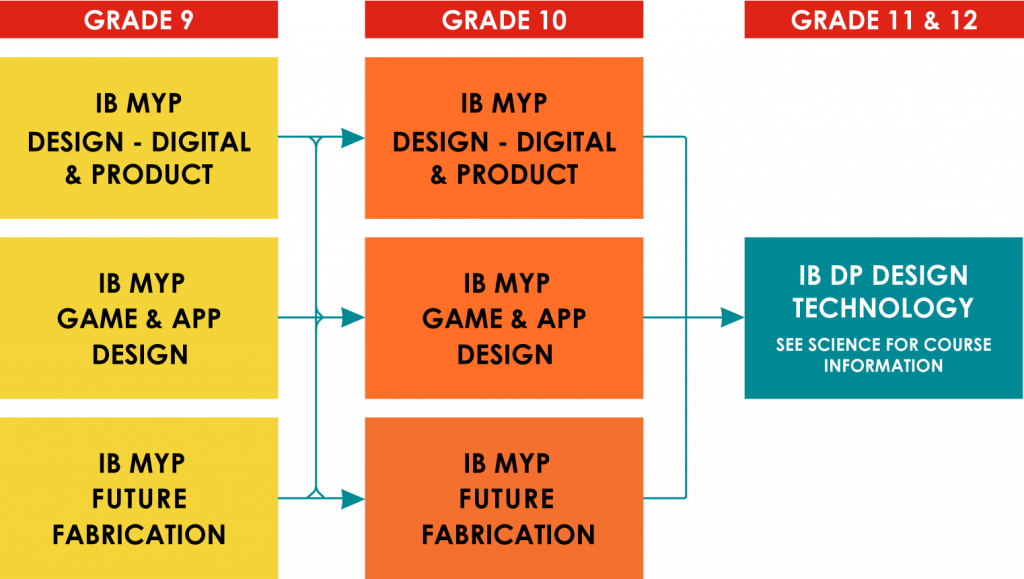
IB MYP Design
MYP Design challenges all students to apply practical and creative thinking skills to solve design problems, encourages students to explore the role of design in both historical and contemporary contexts, and raises students’ awareness of their responsibilities when making design decisions and taking action. MYP Design requires the use of the design cycle as a tool, which provides the methodology used to structure the inquiry and analysis of problems, the development of feasible solutions, the creation of solutions, and the testing and evaluation of the solutions. MYP Design enables students to develop not only practical skills but also strategies for creative and critical thinking.
Grade 9
Content
Grade 9 students complete four units to develop a range of design skills, both product and digital. The first unit, Wild Thing, introduces students to the tools and resources used in High School Design. Other units include a stylized clock design where students draw inspiration from an artist or designer to create a clock for a client, a food design unit where students develop a healthy snack and design the packaging for their snack, and a unit where students use a prototyping platform (Arduino) to build and program a system with inputs and outputs.
Assessment
Students are assessed using the IBMYP Design assessment criteria, which relate specifically to the Design Cycle:
• Criterion A: Inquiring and analyzing
• Criterion B: Developing ideas
• Criterion C: Creating the solution
• Criterion D: Evaluating
Grade 10
Content
Grade 10 students build on the skills they have learned in previous years to creatively design solutions to a range of problems, using both product and digital design. Students focus on solving real world problems in grade 10 so specific units in this course vary from year to year depending on the needs of the WAB community. For the final unit in grade 10 students are given a framework within which they have to identify, analyze and solve a problem. This is a great opportunity for students to explore an area of Design they are interested in and to further develop their skills.
Assessment
Students are assessed using the IBMYP Design assessment criteria, which relate specifically to the Design Cycle:
• Criterion A: Inquiring and analyzing
• Criterion B: Developing ideas
• Criterion C: Creating the solution
• Criterion D: Evaluating
Grades 9 &10 Game and App Development
Game and App Development allows students with a passion for these areas to immerse themselves in a course that dives deeper than a traditional design unit.
The course is structured in a way that offers students the opportunity to direct their own learning. This is made possible by numerous mini-projects that permeate the course, providing students with opportunities for summative assessment at a pace that suits their needs.
Students assume the role of game developers and will use the GameMaker Studio integrated development environment to design, code and test their own games, using a combination of pre-existing assets and their own unique creations. Students will also be able to tap into skills from other subject areas, such as Mathematics, Art, and Music, as they create realistic physics, sprites, and tile sets, as well as sound effects and backing scores.
Assessment
Students are assessed using the IBMYP Design assessment criteria, which relate specifically to the Design Cycle:
• Criterion A: Inquiring and analyzing
• Criterion B: Developing ideas
• Criterion C: Creating the solution
• Criterion D: Evaluating
Grades 9 &10 Future Fabrication
Future allows students with a passion for these areas to immerse themselves in a course that dives deeper than a traditional design unit.
The course is structured in a way that offers students the opportunity to direct their own learning. Students will spend time on robotics and using digital modeling to fabricate physical artefacts. This is made possible by numerous mini-projects that permeate the course, providing students with opportunities for summative assessment at a pace that suits their needs.
Students assume the role of designers and makers, using modern fabrication tools to design, build, and test physical products and systems. Using technologies such as 3D modelling and printing, electronics, robotics, and microcontrollers, students develop functional solutions that respond to real world needs. Students will also draw on skills from other subject areas, including Mathematics and Science, as they prototype mechanisms, program control systems, and refine their ideas through iterative testing and improvement.
Assessment
Students are assessed using the IBMYP Design assessment criteria, which relate specifically to the Design Cycle:
• Criterion A: Inquiring and analyzing
• Criterion B: Developing ideas
• Criterion C: Creating the solution
• Criterion D: Evaluating
