Course Offerings - Science
Science Program Chart
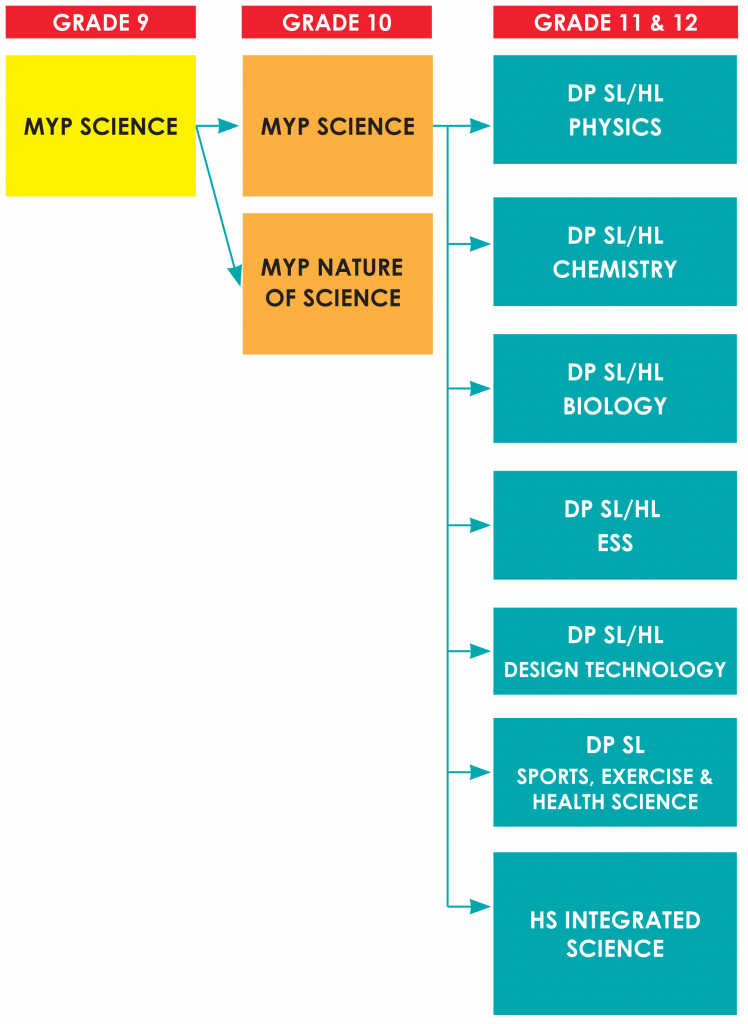
IB MYP Sciences
IB DP Group 4 - Biology, Chemistry, Physics, Environmental Systems And Societies, Design Technology, Sports Science
HS Integrated Science
A fundamental goal of the Science Program is for students to gain scientific literacy by engaging in many of the processes of Science. Scientific literacy involves students making informed judgments and evaluations about scientific issues and using their acquired scientific processing skills for successful problem-solving.
Learning about Science is an active process, incorporating both ‘hands-on’ and ‘mind-on’ experiences. Students actively participate in scientific investigations and use associated skills to formulate scientific explanations. WAB High School students will be exposed to Biology, Physics, Chemistry, and scientific applications throughout the IB MYP Science Program in Grades 9 and 10. The units covered aim to develop in students both a depth of knowledge and the scientific processing skills necessary to prepare them to make scientifically informed decisions later in life and also prepare them for further Science studies.
Upon completion of IBMYP Science in Grade 10, students can make informed choices for Grades
11 and 12 based on their needs. For example, students interested in studying sciences at university may be advised to enroll in two IB Diploma Higher Level science courses.
Students intending to earn an IB Diploma must select and complete two years of an IB Group 4 Science course at either Higher Level or Standard Level. Students intending to earn a certificate in IB Science must also complete a two-year course at either Higher Level or Standard Level.
Students not wishing to do a full IB Diploma Science course are able to take Integrated Science.
Grades 9 and 10
The Science (IB MYP) course is an integrated approach to Biology, Physics, Chemistry, and Environmental Sciences based on an inquiry framework. The course sets the foundation for more advanced High School science studies in Grades 11 and 12. Students develop the skills and processes necessary to undertake scientific investigations while developing an understanding of the concepts of science. This encourages a globally responsible attitude towards both natural and man-made environments.
Content
Topics and guiding questions that may be covered include:
Grade 9 Science
Students will study units that incorporate physics, chemistry, biology, and ecology using an interdisciplinary-based approach.
Grade 10 Science
Students will study units that incorporate physics, chemistry, biology, earth and space science, ecology, and evolution using an interdisciplinary-based approach.
Grade 10 Nature of Science
In each semester of the course, students will develop and implement their own in-depth science inquiry projects, reaching for a high level of knowledge and understanding. Through this experience, students set their lines of inquiry and develop research and practical skills in an area of interest. They are assessed using the MYP sciences criteria.
Assessment
Summative assessment tasks cover four assessment criteria:
• Criterion A: Knowing and understanding
• Criterion B: Inquiring and designing
• Criterion C: Processing and evaluating
• Criterion D: Reflecting on the impacts of science
Grades 11 and 12
HS Integrated Science
The course will be divided into thematic units of work designed by the teacher with input from the students based on their interests. Core topics over the two years may include: the nature of science, forensic science, health science, food science, sustainability and an independent investigation.
Assessment
Throughout the course students will be immersed in scientific inquiry and problem based learning. They will be involved in practical experiments as well as research and data-based investigations both on an individual and group basis. Students will have the opportunity to showcase their learning in creative ways of their choice. This may include written reports, infographics, animations, videos and presentations
to name a few. At the end of their first year, students will have acquired enough skills to design and implement their own investigation into a topic of their choice. They will present the results of this inquiry at the beginning of the second year as an exemplar of science in action to the new students in year one.
The students are assessed on four criteria each semester:
• Knowledge & Understanding – 25%
• Thinking & Investigation – 25%
• Communication – 25%
• Application – 25%
The Experimental Sciences IB DP Courses
Experimental Sciences (IB DP) aims to enable students to apply and use a body of knowledge and scientific investigative methods while developing an ability to analyze, evaluate, and synthesize scientific information. All IB DP Sciences are 2-year courses that may be undertaken at either a Higher Level (HL) or Standard Level (SL). Each involves both Core and Option Topics. All IB DP Sciences require that students complete the Group 4 Research Project as part of their Practical Investigations.
Higher Level Courses require the completion of 60 hours of Practical Investigations within the overall two-year course work in Biology, Chemistry, Physics, Design Technology, or Sports & Exercise Health Science (SEHS).
Standard Level Courses require the completion of 40 hours of Practical Investigations in Biology, Chemistry, Design Technology, Physics, or Sports & Exercise Health Science (SEHS) within the overall two-year coursework
Assessment
Internal Assessment
Internal Assessment in the IB DP Experimental Sciences will be based upon the IB Diploma Assessment criteria for Practical reports in the areas of:
• Personal Engagement
• Exploration
• Analysis
• Conclusion & Evaluation
• Communication
All of the criteria are developed and assessed throughout the 2 years and are part of the students’ WAB grades. In grade 11 or 12 students carry out a formal internal assessment. The internal assessment constitutes 20% of the final assessment in Biology, Chemistry, and Physics, 25% of the final assessment in Environmental Systems and Society (ESS), and 24% of the final assessment in Sports and Exercise Health Science.
External Assessment
At the completion of the two-year course, students are required to sit three IB External Examination papers:
• Paper 1 consists of multiple-choice questions
• Paper 2 includes a data-based question, short answer questions, and extended response questions
The external examination constitutes 80% of the final assessment of the Biology, Chemistry, Physics, and Sports & Exercise Health Science courses, and 75% of the Environmental Systems and Society (ESS) course.
In order to prepare students for the External Examinations at the completion of the two-year course, students will undertake throughout the two-year period, school-based topic tests and examinations consisting of multiple choice, short answer, and long answer questions that mirror the IB External Examinations in the Group 4 Sciences.
IB DP Biology HL & SL
The Biology courses allow the student to continue the study of biology, examining living organisms and systems.
Content
Core topics of both SL and HL courses are Cells, Molecular Biology, Genetics, Ecology, Evolution and Biodiversity, and Human Physiology. Additional HL Core Topics are Nucleic Acids, Metabolism, Cell Respiration and Photosynthesis, Genetics and Evolution, Animal Physiology, and Plant Science.
Additionally, one Option Topic must be undertaken, which may include: Neurobiology and Behavior, Ecology and Conservation, Biotechnology and Bioinformatics, or Further Human Physiology.
IB DP Chemistry SL & HL
Typically, Chemistry is a prerequisite for many other courses in higher education, such as medicine, biological sciences, engineering, and environmental science.
Content
Core Topics of both SL and HL Chemistry courses are: Stoichiometric relationships, Atomic structure, Periodicity, Chemical bonding and structure, Energetics/thermochemistry, Chemical kinetics, Equilibrium, Acids and bases, Redox processes, Organic chemistry and Measurement and data processing.
Additional HL Core Topics are: Atomic structure, The periodic table – the transition metals, Chemical bonding and structure, Energetics/thermochemistry, Chemical kinetics, Equilibrium, Acids and bases, Redox processes, Organic chemistry, and Measurement and analysis.
Both HL and SL students must also undertake one option, which may include Materials, Biochemistry, Energy, or Medicinal chemistry.
IB DP Physics SL & HL
While the Physics topics in Grades 9 and 10 tend to focus on areas of classical physics, such as the building blocks of Newtonian mechanics, IBDP Physics revisits these concepts in more detail and moves forward into the areas of thermal physics, electromagnetism, and quantum mechanics. Typically, Physics is a prerequisite for many sciences and engineering courses at university.
Content
Core IB DP Physics Topics include Measurements and uncertainties, Mechanics, Thermal Physics, Waves, Electricity and magnetism, Circular motion and gravitation, Atomic, nuclear, and particle physics, and Energy production.
Additional HL core topics include options in the following fields: Wave phenomena, fields, electromagnetic induction, and quantum and nuclear physics.
Students also undertake one option from the following topics: Relativity, Engineering Physics, Imaging, or Astrophysics.
Environmental Systems & Societies SL (IB DP)
Environmental Systems and Societies (IB DP) is a transdisciplinary course and can be counted as both a Group 3 and Group 4 subject for the IB Diploma. It is only offered at the standard level. The course requires 30 hours of practical investigations within the overall two-year course work.
The aims of the course are to:
• Promote understanding of environmental processes at a variety of scales, from local to global
• Provide a body of knowledge, methodologies, and skills that can be used in the analysis of environmental issues at local and global levels
• Enable students to apply the knowledge, methodologies, and skills gained
• Promote critical awareness of a diversity of cultural perspectives
• Recognize the extent to which technology plays a role in both causing and solving environmental problems
• Appreciate the value of local as well as international collaboration in resolving environmental problems
• Understand that environmental issues may be controversial, and may provoke a variety of responses
• Appreciate that human society is both directly and indirectly linked to the environment at a number of levels and at a variety of scales
Content
The topics covered include: Systems and Models, the Ecosystem, Human Population, Carrying Capacity and Resource Use, Conservation and Biodiversity, Pollution Management, the Issue of Global Warming, and Environmental Value Systems.
Assessment
Internal assessment in Environmental Systems and Societies will be based on the IB Diploma assessment criteria in the areas of:
• Planning
• Data collection and processing
• Discussion, evaluation, and conclusion
• Personal skills
The internal assessment constitutes 20% of final assessment.
At the completion of the two-year course students are required to sit two external IB examination papers.
• Paper 1 consists of short-answer and data-based questions
• Paper 2 consists of a case study and essay questions
The external examination constitutes 80% of the final assessment.
Sports & Exercise Health Science SL/HL (IB DP)
The Sports & Exercise and Health Science course will teach students about how the Human body works in relation to the concepts and functions that are related to sport, health, and physical activity. Students will need to study 6 of the core topics and then choose 2 other options.
Core
There are six compulsory topics in the core:
• Anatomy
• Exercise
• physiology
• Energy systems
• Movement analysis
• Skill in sport and Measurement and evaluation of human performance
Options
There are four options. Students are required to study any two options.
• Optimizing physiological performance
• Physical activity and health
• Nutrition for sport, exercise and health
